Tramadol tablets are analgesic medicines that are given in clinical conditions to relieve severe-to-moderate pain. They are good painkillers, and the tablets are included in the treatment plan for various diseases, postoperative management, injury, and long-term pain. Anybody taking these tablets must know how they work in the brain and body. They are good painkillers, but tramadol is also addictive if misused.
In this blog, we are going to tell you how Tramadol 50 mg tablets impact the brain, how they work, and why this drug is so addictive.
It is a pain reliever in the opioid class of drugs based on tramadol descriptions found online. It is part of the opioids containing centrally acting drugs, which act both in the brain and spinal cord to mitigate pain. Tramadol 50 mg tablets are used for people with acute and chronic pain, since other opioids may not manage pain adequately.
Tramadol 50 mg tablets are generally considered for treating moderate-to-severe pain. Tramadol is a very beneficial pain reliever, often sought by people looking for an alternative solution instead of stronger opioids. The most prominent benefits of using Tramadol 50 mg tablets for pain management include the following:
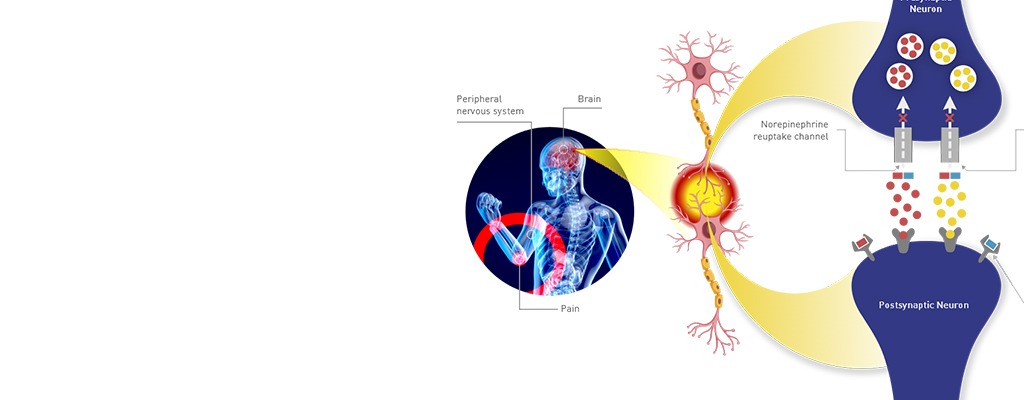
Pain is therefore a multifaceted phenomenon by which the brain processes injury or illness. Tramadol 50 mg tablets act on the pathways in the brain, which is why this medicine is useful for treating different types of pain.
Because it is a strong analgesic, tramadol is ideal for use in cases of pain due to injuries, surgeries, or sudden-onset illnesses. The conventional formulation enters the body and rapidly interrupts pain messages to relieve the patient.
Severe pain that comes with arthritis, fibromyalgia, or nerve damage, requires long-span release of the drug, which the extended-release tramadol offers. Because the levels of the drug are constant in the patient’s system, this lessens the number of required administrations, making the patient more comfortable.
Though they are medically beneficial in relieving pain, tramadol tablets contain addictive features, especially when abused or taken for a long time. Explaining the dependency-producing effects of tramadol involves an analysis of the effects of the drug on the brain’s reward system.
1. Effect on Mood and Emotions
Tramadol can affect mood by increasing levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, which may cause feelings of euphoria or emotional well-being. This combination of mood improvement and pain relief can be appealing to people who want to escape both physical pain and emotional distress. However, these effects can also make tramadol tempting to misuse, as some individuals may seek the emotional relief it provides.
2. Tolerance Development
As with all the other opioids, tolerance will be a consequence of the long-term consumption of tramadol. This is the factor that makes the body tolerant of the drug, and higher doses of the drug are needed to get an equal amount of painkillers. Doubling the dose without a medical practitioner’s advice significantly increases the risk.
While tramadol is safer when compared to the more powerful opioids, misuse of the drug can similarly result in significant harm to the patient. Misuse is measured in terms of taking too much, taking it illegally, or taking it with other drugs.
Too much tramadol overstimulates opioid receptors in the brain and leads to respiratory depression (slowing or stopping breathing), unconsciousness, or death. Overdose is particularly dangerous when tramadol is combined with alcohol, other opioids, or sedatives.
Tablet tramadol in high doses has the potential to induce seizures, especially in those with seizure disorders or on other drugs lowering the seizure threshold.
Tramadol’s action on serotonin levels will most likely result in serotonin syndrome, which can be life-threatening. It presents with confusion, tachycardia, hypertension, and rigidity. This is more likely to occur when combined with antidepressants or other drugs that raise serotonin levels.

To reduce the risks of tramadol, one must use it responsibly on the doctor’s prescription. The most important things are mentioned below:
Flawless adherence to the above enables taking advantage of the pain-relief action of tramadol without experiencing addiction and abuse.
Tramadol 50 mg tablet is a potent painkiller medication with substantial relief from severe to mild pain by biphasic activity at opioid receptors and neurotransmitters. Their ingestion also possesses the potential of addiction if not responsibly or incessantly taken.
The discussion of how tramadol works in the brain allows one to understand its benefits and drawbacks. In the hospital, tramadol is administered in a way that allows patients to experience effective as well as safe relief from pain without jeopardizing their health.
On the path to pain relief, adequate use of medication like tramadol provides comfort without any adverse effect on future health. Always request your doctor to ask whether a 50 mg tablet would help meet your pain relief requirement.
1. Is tramadol a strong painkiller?
Tramadol is a moderate painkiller, not as strong as opioids like morphine.
2. Is tramadol stronger than morphine?
No, tramadol is weaker than morphine.
3. Is tramadol a full opioid?
No, tramadol is a partial opioid, meaning it doesn’t work as strongly as full opioids.
4. What are the side effects of tramadol?
Side effects can include dizziness, nausea, constipation, headache, and risk of addiction.
Hello! We now offer bank payments. Send a message here to open your WhatsApp to know how!